Water Quality Challenges in Timbulsloko Village: The Impact of Seawater Intrusion and Human Activities
Water Quality Challenges in Timbulsloko Village: The Impact of Seawater Intrusion and Human Activities
Coastal communities worldwide face increasing threats to their water resources, and Indonesia’s Timbulsloko Village presents a compelling case study of these challenges. Recent research reveals alarming water quality conditions that demand urgent attention from multiple stakeholders.
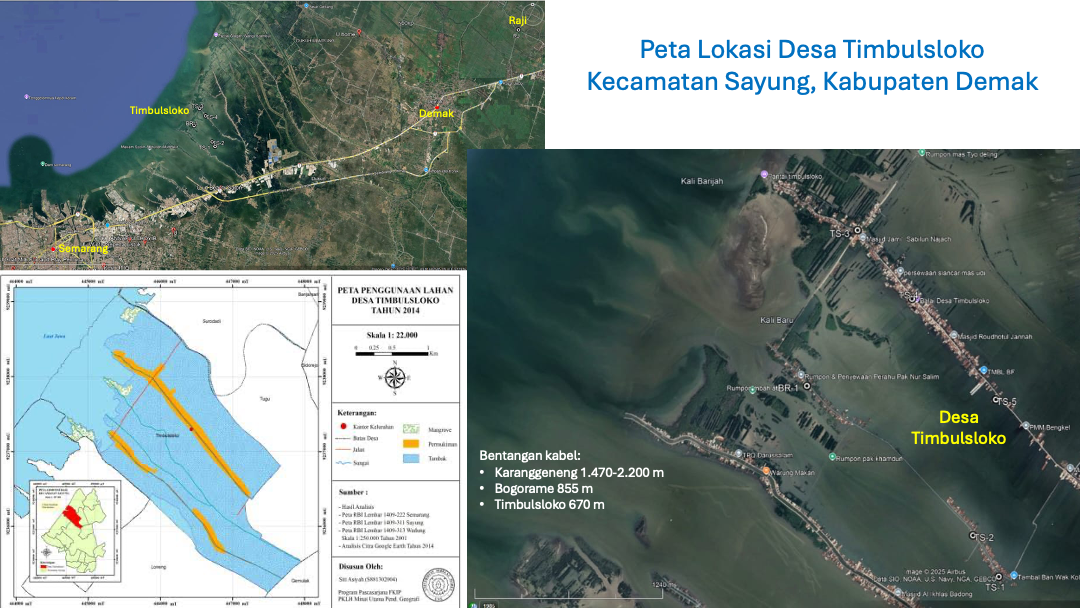
The team consisting of Arif Susanto, ST., MT. and undergraduate Geology Engineering student Sultoni attempted to map the groundwater situation in Timbulsloko Village.

Concerning Water Quality Findings
Water analysis from two sampling locations (TS-1 and BR-1) shows multiple parameters exceeding recommended thresholds. Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) reached 543 mg/L at TS-1 and a concerning 1394 mg/L at BR-1, significantly above the permissible limit. These elevated mineral contents affect water palatability and usability.
Sodium concentrations were found at 187.48 mg/L in TS-1, rising dramatically to 446.09 mg/L in BR-1, indicating high salinity levels particularly in areas frequently affected by tidal flooding. BR-1 also showed high chloride (472.29 mg/L) and sulfate (329.92 mg/L) levels.
Microbiological testing revealed Total Coliform counts of 4 CFU/100 mL at BR-1, exceeding safe drinking water standards of 0 CFU/100 mL, suggesting contamination from poor sanitation systems or urban runoff.
Root Causes
Seawater intrusion emerges as the dominant factor affecting water quality, exacerbated by land subsidence and increased salinity from climate change impacts. The North Java Coast’s geological characteristics, consisting of unconsolidated sediments, make it vulnerable to natural compaction, subsidence, and erosion.
Human activities such as mangrove deforestation and aquaculture expansion significantly contribute to water quality degradation by reducing natural coastal defenses and facilitating more severe seawater intrusion.
Moving Forward: Essential Actions
To address these challenges, several critical steps must be taken:
- Develop water treatment infrastructure to ensure clean water supplies for communities in subsiding coastal villages.
- Monitor and regulate groundwater extraction to mitigate subsidence through sustainable management practices.
- Restore mangrove ecosystems as natural buffers against coastal erosion, tidal flooding, and saltwater intrusion.
- Implement community-based adaptation strategies including education initiatives and participatory monitoring programs.
The Timbulsloko case should serve as a warning call for integrated coastal management and proactive environmental governance. Coordinated action across multiple sectors is needed to address these complex, interconnected challenges before they reach irreversible tipping points.
Hits: 9